Reporte de caso
Autores
CG Nogales, MB Ferreira, FUF Campos, M Siqueira, SB Macedo
Resumen
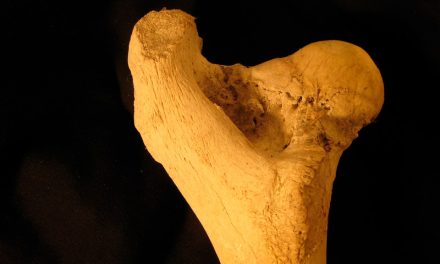
INTRODUCTION: An injury to the tooth-supporting structures results in increased mobility, but without displacement of the tooth. Bleeding in gingival sulcus is a pathognomonic signal. The tooth is positive to a percussion test. Follow-up is required to test dental vitality. When pulp necrosis occurs, root canal treatment is indicated. Ozone therapy comes as a new possibility in root canal treatment to promote high disinfection and increase apical healing. This manuscript reports a subluxation case followed by pulp necrosis with an extended apical radiolucent image.
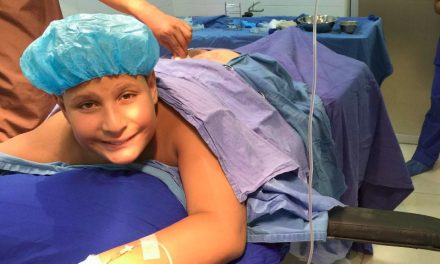
CASE REPORT: During conventional root canal treatment, 100 mL of 16 µg/mL ozonated water and 100 mL of 40 µg/mL ozone gas were applied into the root canal, and calcium hydroxide dressing was used. Apical radiolucent image decreased into 40 days. According to the literature and clinical data, ozone therapy has a great potential to be incorporated into endodontic therapy. Its biostimulator effects and antimicrobial potential are evident and corroborated by the literature.
CONCLUSION: According to the literature and the case report, ozone therapy is suitable to be used as an adjuvant to root canal treatment
This post is also available in:  English (Inglés)
English (Inglés)