Original paper
Author
Leslie Elena Sánchez Gallardo, Daniel Talamás Lara
Abstract
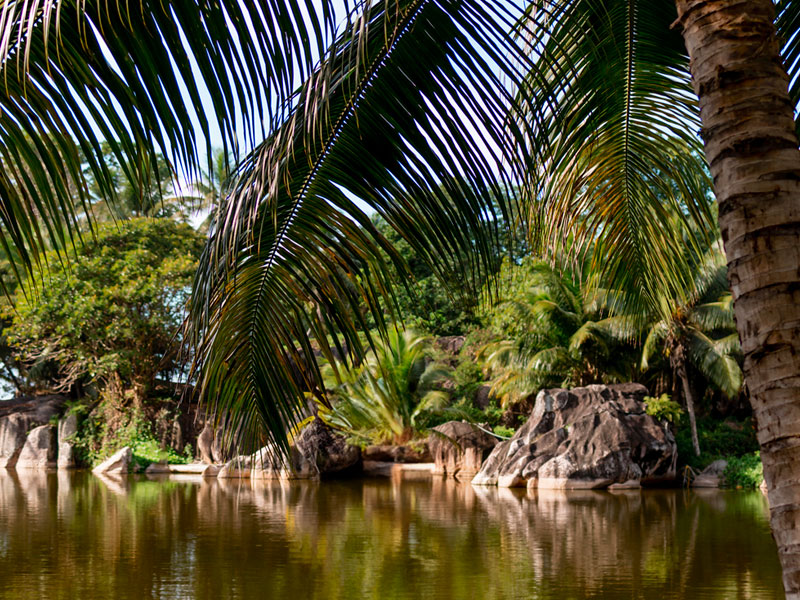
Amebiasis is a major health problem, especially in tropical countries, and is considered the third leading cause of death among parasitic diseases worldwide. Amebiasis is manifested by the transmission of Entamoeba histolytica cysts through the fecal-oral route from contaminated water or food. Ozone therapy consists of the application of a mixture of medical oxygen with ozone, which is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen O3. Among the biological effects of ozone, the first place is traditionally occupied by the germicidal effect. This action of ozone acts when applied externally, following the various therapeutic modalities, mainly in high concentrations. The first target of ozone is the plasma membranes of the cell and the modifications induced by ozone in the intracellular content, i.e., oxidation of cytoplasmic proteins and alteration of the functions of the organs.
In this study it was possible to demonstrate by means of different microscopic techniques the impact of ozone on amoeba, finding the damage to membranes, as well as the different reactions that it has to reach the final objective which is the death of the trophozoites. With the differences between each of the techniques and doses used for this experiment, significant results were found to suggest the germicidal use of ozone, particularly against E. histolytica parasitosis.
This post is also available in:  Español (Spanish)
Español (Spanish)